
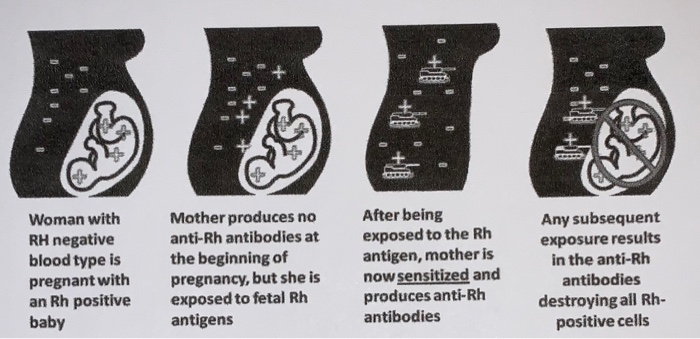
The immunoglobulin breaks down the baby's red blood cells inside the mother's bloodstream before her immune system has time to react. HDN is now rare, since Rh-negative mothers are immunised throughout their pregnancy and within 72 hours of giving birth, using an immunoglobulin made from donated blood products. Preventing haemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) This is called haemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN). If left untreated, this can result in severe anaemia or even death of the baby. These antibodies then destroy the baby's red blood cells.
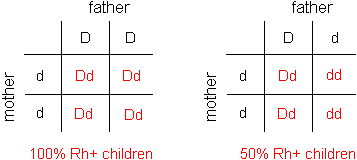
If the woman later conceives another Rh-positive baby, her immune system will flood the fetus with antibodies. Specialised white blood cells will make antibodies designed to kill Rh-positive blood cells. If blood cells from the baby travel across the placenta, the woman's immune system will see the Rh-positive cells as a threat. Problems can occur during pregnancy if an Rh-negative woman carries an Rh-positive baby. Australia has one of the safest blood supplies in the world, and donating blood here is a very safe process.
O negative red blood cells can be given to anybody if necessary, but it is always preferable to match the exact blood group. Transfusions are of red blood cells or other components such as plasma or platelets. Blood groups in AustraliaĪ person's blood group is described by the appropriate letter (A, B, AB or O) and by whether their blood is Rh-positive or Rh-negative.Īccording to Australian Red Cross Lifeblood, the percentage of blood group frequency in Australia is:Ī blood transfusion is the transfer of blood or blood components from one person to another. A person who is Rh-negative will experience a severe immune-system reaction if Rh-positive blood gets into their bloodstream. Your Rh type is determined by a different pair of genes to the ones that determine your ABO blood type (again, one inherited from each parent).īlood is either Rh-positive or Rh-negative, depending on whether certain molecules are present. Rh type blood factorĪ person's blood type used to be called their 'Rhesus type' but now we say 'Rh type'. When a person needs a blood transfusion, the donated blood must match the recipient's blood or complications will occur. A person's blood group is determined by a pair of genes - one gene inherited from each parent.Įach blood group is identified by its own set of molecules (called antigens), which are located on the surface of red blood cells. The 4 different blood groups in the ABO system are A, B, AB and O. Other blood group systems exist - to date, researchers have identified more than 300 minor blood groups with new antigens still being discovered. Together, they make up the 8 main blood groups. The 2 main ways to classify blood groups are the ABO system and the Rh system. Floating in the plasma are the red blood cells that carry oxygen, the white cells that form part of the immune system, and clotting cells called platelets. The bulk of your blood is made up of plasma. The blood carries oxygen and nutrients to every cell in the body and picks up waste products (such as carbon dioxide) for removal from the body. The circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels and blood.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
